Worker Bee
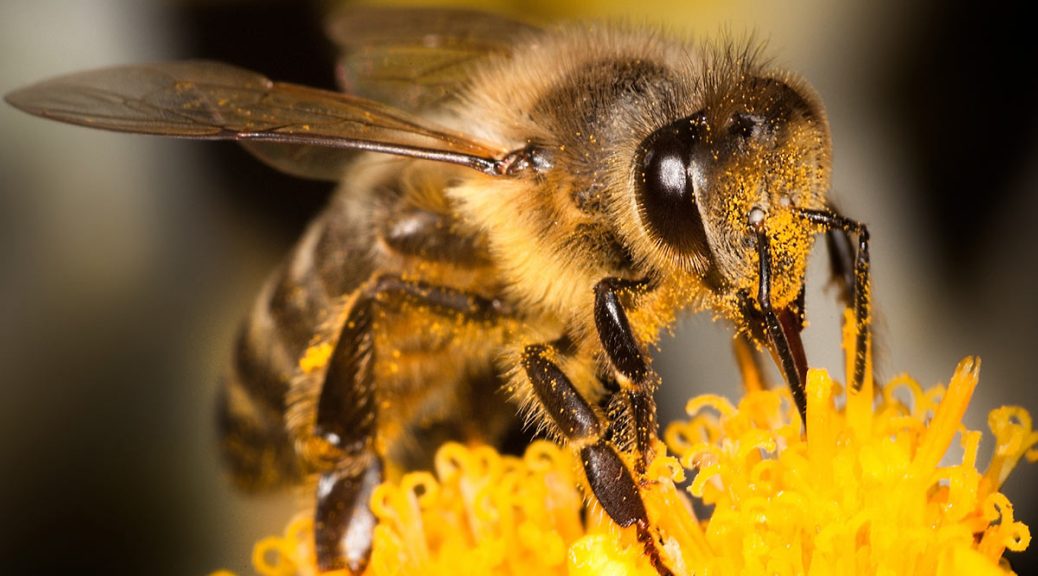
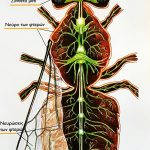
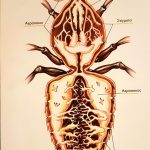
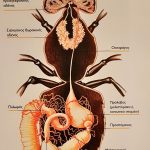
Worker bees are the busiest members of a honey bee colony. These female bees are responsible for performing a variety of tasks that are essential for the survival and growth of the colony.
One of the primary roles of worker bees is foraging for food. They search for nectar, pollen, and water and bring it back to the hive to feed the rest of the bees. Worker bees also take care of the brood, which includes feeding and grooming the young bees and maintaining the temperature and humidity of the hive.
In addition to these tasks, worker bees also play a key role in the hive’s defense. They secrete a chemical called pheromone that helps to deter predators and mark the location of food sources. They also use their stingers to protect the hive if necessary.
Despite their tireless work, worker bees have a relatively short lifespan. Most worker bees live for just a few months, during which they perform a variety of tasks within the hive. However, as the winter approaches and the colony’s population begins to decline, some worker bees may live for several months to help ensure the survival of the hive through the colder months.
Overall, worker bees are vital to the success of a honey bee colony. Without their tireless work and dedication, the hive would not be able to thrive.